| <template> |
| <manage-listsv-model='items'> |
| <templatescope='{ item: user }'> |
| {{ user.firstName }} {{ user.lastName }} |
| template> |
| manage-lists> |
| template> |
| <script> |
| exportdefault { |
| components: { |
| ManageLists |
| }, |
| data() { |
| return { |
| items: [ |
| { firstName:'John', lastName:'Doe' }, |
| { firstName:'Renae', lastName:'McGillicuddy' } |
| ] |
| }; |
| } |
| } |
| script> |

Working with nested routes can be quite a hassle. Therefore I did come up with a conclusion on how to keep the routing configuration clean and to ease the working with nested routes. There are already some tutorials on how to work with Vue Router in general, but I want to focus on this specific issue and the architecture around it. Nested scoped slots in Vue templates. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets. In vue.js props are used to pass the data to its child components, but it is hard to pass when we have a complex code. In such cases slots can be used. Let's create a new component called Post by adding the slot element. I have to create multiple tabs having dynamic content. There will be one parent component to handle switching between tabs and master data for tabs. This parent-child component system is to be used as a generic component which accepts a list about tabs and renders tabs as per the list. I can use this parent component in my root component where tabs list information is available and also the.
| <template> |
| <div> |
| <token-list :value='items' @input='forwardInput'> |
| <templatescope='props'> |
| <slotv-bind='props'>slot> |
| template> |
| token-list> |
| <formclass='form' @submit.prevent='handleAdd'> |
| <inputtype='text'placeholder='New Item'v-model='newItem'ref='newItem' /> |
| <buttontype='submit'>Add Itembutton> |
| form> |
| div> |
| template> |
| <script> |
| importTokenListfrom'./TokenList'; |
| exportdefault { |
| props: { |
| value: { |
| type:Array, |
| default() { |
| return []; |
| } |
| } |
| }, |
| components: { |
| TokenList |
| }, |
| methods: { |
| handleAdd() { |
| this.$emit( 'input', this.value.concat( this.newItem ) ); |
| this.newItem=''; |
| this.$refs.newItem.focus(); |
| }, |
| forwardInput( payload ) { |
| this.$emit( 'input', payload ); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| script> |
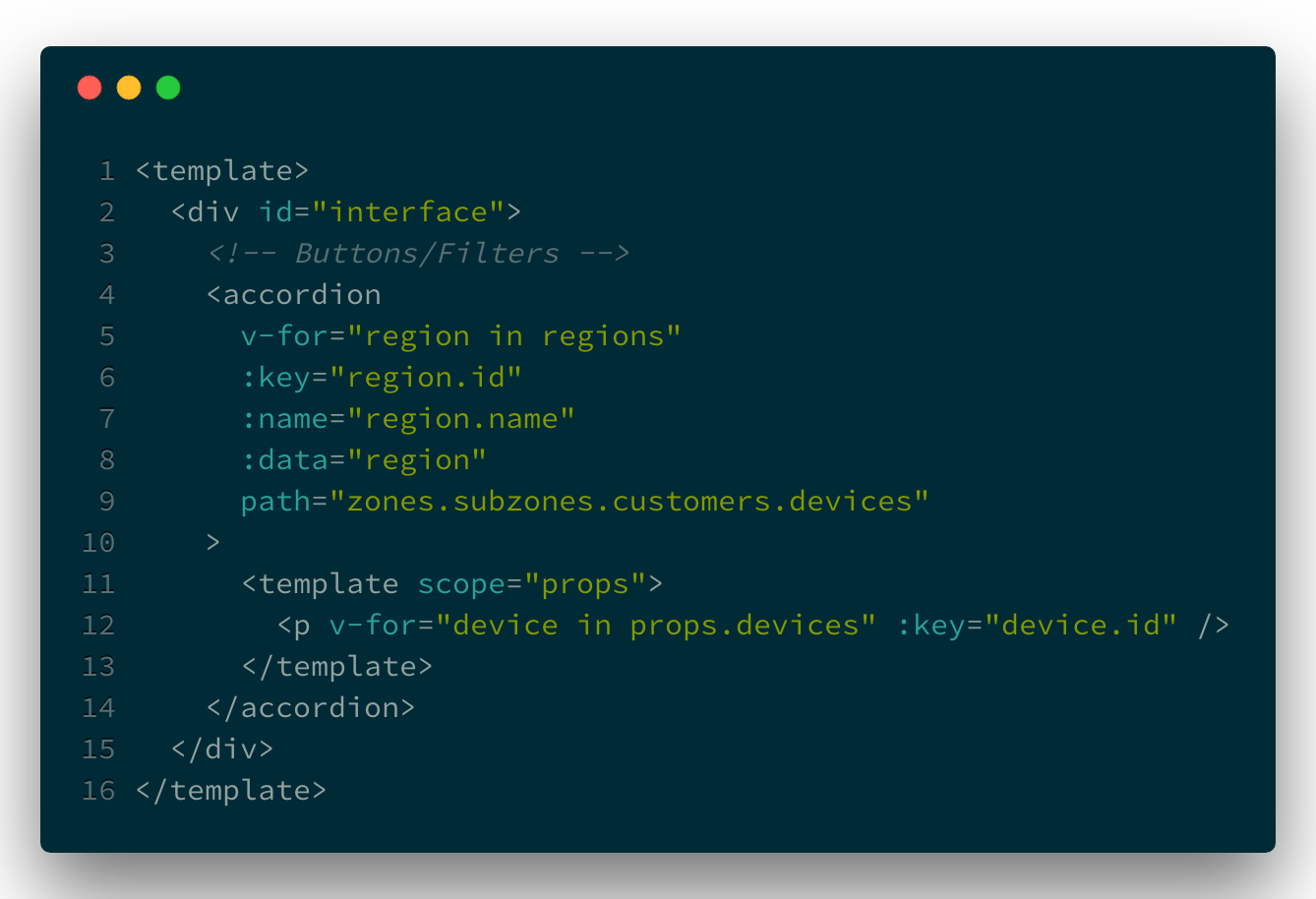
| <template> |
| <divclass='token-list clearfix'> |
| <divv-for='( item, index ) in value'class='token-item'> |
| <slot :item='item' :index='index'> |
| <span>{{ item }}span> |
| <buttontype='button' @click='remove( index )'>×button> |
| slot> |
| div> |
| div> |
| template> |
| <script> |
| exportdefault { |
| props: { |
| value: { |
| required:true |
| } |
| } |
| methods: { |
| remove( index ) { |
| this.$emit( 'input', [ |
| ..this.value.slice( 0, index ), |
| ..this.value.slice( index +1 ) |
| ] ); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| script> |
In this tutorial, we will learn about how to use the slots in vue.js with the help of examples.
What are Slots?

Slots helps us to pass the data between opening and closing component tags.
In vue.js props are used to pass the data to its child components, but it is hard to pass when we have a complex code. In such cases slots can be used.
Let's create a new component called Post by adding the element.
Now, if we pass any content between the Post component opening and closing tags that are rendered in the place of element.
Output:
Named Slots
Sometimes, we need to pass the data to a specific places in such cases named slots can be used.
The named slots can be created by adding a name attribute to the element.

To pass the content to the named slots we need to use v-slot directive on template providing slot name as v-slot argument.
Fallback data

Working with nested routes can be quite a hassle. Therefore I did come up with a conclusion on how to keep the routing configuration clean and to ease the working with nested routes. There are already some tutorials on how to work with Vue Router in general, but I want to focus on this specific issue and the architecture around it. Nested scoped slots in Vue templates. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets. In vue.js props are used to pass the data to its child components, but it is hard to pass when we have a complex code. In such cases slots can be used. Let's create a new component called Post by adding the slot element. I have to create multiple tabs having dynamic content. There will be one parent component to handle switching between tabs and master data for tabs. This parent-child component system is to be used as a generic component which accepts a list about tabs and renders tabs as per the list. I can use this parent component in my root component where tabs list information is available and also the.
| <template> |
| <div> |
| <token-list :value='items' @input='forwardInput'> |
| <templatescope='props'> |
| <slotv-bind='props'>slot> |
| template> |
| token-list> |
| <formclass='form' @submit.prevent='handleAdd'> |
| <inputtype='text'placeholder='New Item'v-model='newItem'ref='newItem' /> |
| <buttontype='submit'>Add Itembutton> |
| form> |
| div> |
| template> |
| <script> |
| importTokenListfrom'./TokenList'; |
| exportdefault { |
| props: { |
| value: { |
| type:Array, |
| default() { |
| return []; |
| } |
| } |
| }, |
| components: { |
| TokenList |
| }, |
| methods: { |
| handleAdd() { |
| this.$emit( 'input', this.value.concat( this.newItem ) ); |
| this.newItem=''; |
| this.$refs.newItem.focus(); |
| }, |
| forwardInput( payload ) { |
| this.$emit( 'input', payload ); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| script> |
| <template> |
| <divclass='token-list clearfix'> |
| <divv-for='( item, index ) in value'class='token-item'> |
| <slot :item='item' :index='index'> |
| <span>{{ item }}span> |
| <buttontype='button' @click='remove( index )'>×button> |
| slot> |
| div> |
| div> |
| template> |
| <script> |
| exportdefault { |
| props: { |
| value: { |
| required:true |
| } |
| } |
| methods: { |
| remove( index ) { |
| this.$emit( 'input', [ |
| ..this.value.slice( 0, index ), |
| ..this.value.slice( index +1 ) |
| ] ); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| script> |
In this tutorial, we will learn about how to use the slots in vue.js with the help of examples.
What are Slots?
Slots helps us to pass the data between opening and closing component tags.
In vue.js props are used to pass the data to its child components, but it is hard to pass when we have a complex code. In such cases slots can be used.
Let's create a new component called Post by adding the element.
Now, if we pass any content between the Post component opening and closing tags that are rendered in the place of element.
Output:
Named Slots
Sometimes, we need to pass the data to a specific places in such cases named slots can be used.
The named slots can be created by adding a name attribute to the element.
To pass the content to the named slots we need to use v-slot directive on template providing slot name as v-slot argument.
Fallback data
In some cases, we can use fallback data (aka default) when data is not passed to a slot.
For example:
In the above component, we have added a Submit text inside a slot element.
Now, If we use a my-button component without passing any data we can seethe fallback data Submit text is rendered inside the button.
Places to eat around mystic lake casino. Output of rendered html:
Nested Slots Vue Js 2.2
But, if we pass data to the my-button component fallback data is replaced.
Nested Slots Vue Js Tool
Output of rendered html:
